
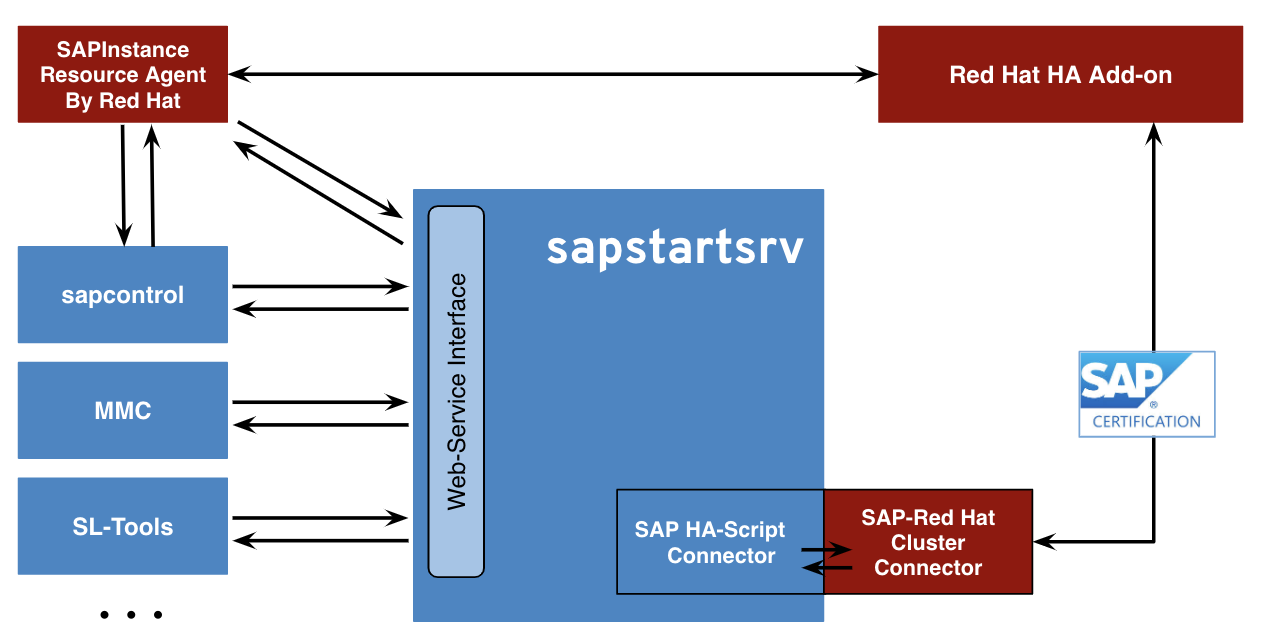
Next, open the hosts file for editing with the command: Once you’ve set the hostname, log out and log back in. Where HOSTNAME is the hostname to be used (such as kubemaster or kubenode). The first thing to do is set the hostnames of your servers and then modify the /etc/hosts file.
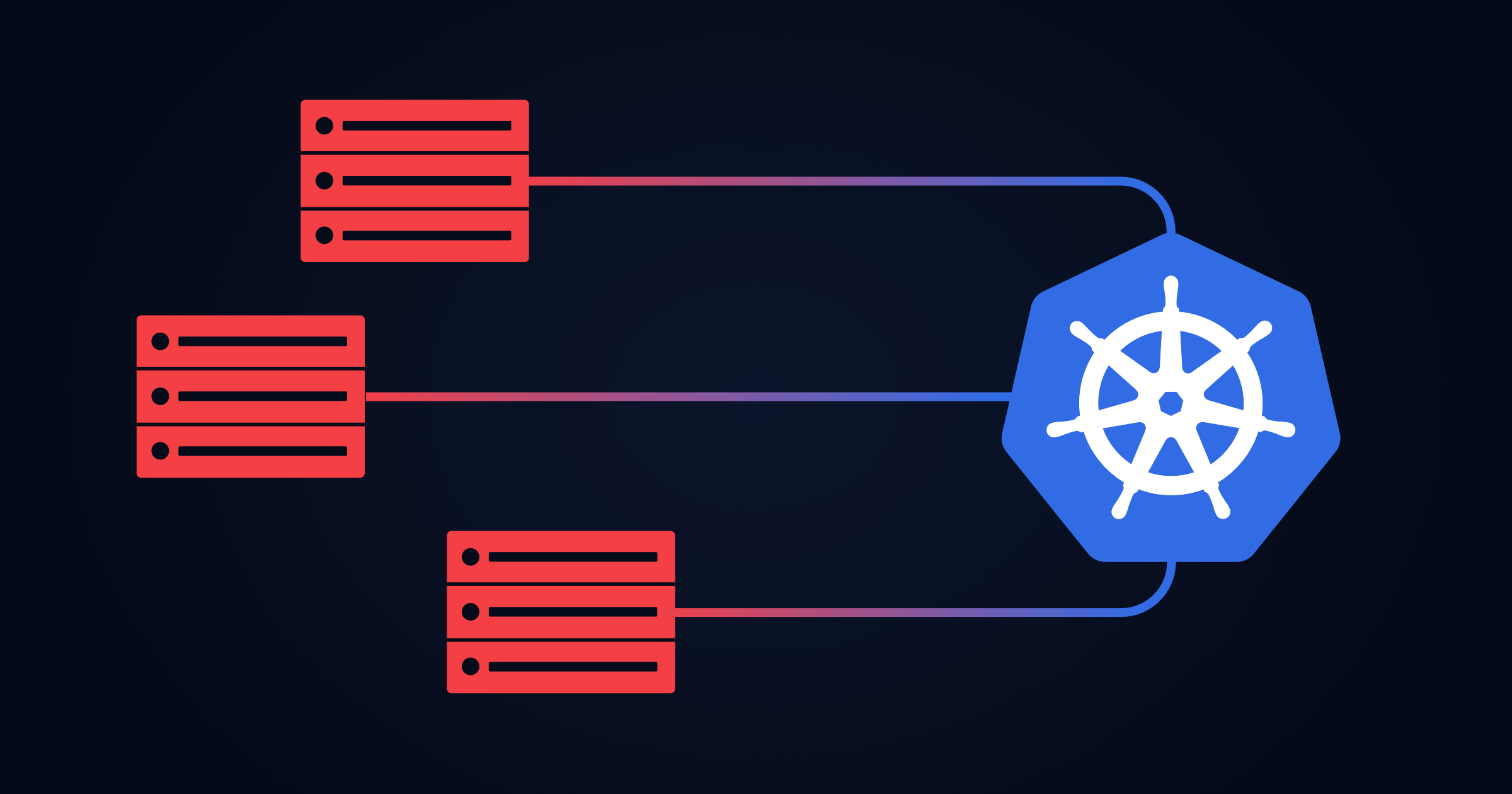
Unless otherwise noted, you’ll take care of everything below on both the master and nodes. With all of that in hand, let’s get to work. You’ll also need a user account with sudo privileges and access to the root user account. I’ll be demonstrating on two CentOS 8 servers, running on IP addresses: In order to successfully install Kubernetes (and create a cluster), you’ll need at least two machines. If you’re looking to deploy a Kubernetes cluster on CentOS 8, the changes made to the operating system will directly affect you.īut how? Although they don’t change the way you deploy the actual cluster, getting everything in place for the deployment is quite different.įear not, I’m going to walk you through the process of installing Kubernetes on CentOS 8, so you can then get back to the business of deploying your cluster and managing your containers. Such is the case with installing Kubernetes. Many of those changes have caused admins to approach their tasks differently. I you are running a lot of administrative commands you can allow password-less sudo: echo " ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL"> /etc/sudoers.If you’ve migrated over from Red Hat’s CentOS 7 to CentOS 8, you’ve probably noticed a lot of changes have taken place. On worker nodes: sudo docker run -d -privileged -restart=unless-stopped -net=host -v /etc/kubernetes:/etc/kubernetes -v /var/run:/var/run rancher/rancher-agent:v2.1.0-rc9 -server -token TOKEN -ca-checksum CHECKSUM -worker

Log on to the Rancher manager node and create a Custom cluster in the Rancher web interface ( From my own existing nodes).Īdd controllers and workers following the instructions.įor example, on controller nodes that include etcd: sudo docker run -d -privileged -restart=unless-stopped -net=host -v /etc/kubernetes:/etc/kubernetes -v /var/run:/var/run rancher/rancher-agent:v2.1.0-rc9 -server -token TOKEN -ca-checksum CHECKSUM -etcd -controlplane On rancher manager node only: docker run -d -name rancher -restart=unless-stopped -p 80:80 -p 443:443 rancher/rancher:v2.1.0-rc9 Note this will cause authentication problems now or in the future. If you want to clone this VM for the k8s nodes poweroff and snapshot. Subscription-manager repos -enable rhel-7-server-extras-rpms Install Docker on all of the host machines: yum upgrade -y


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
